Split Tunneling vs Full Tunneling: How to Pick the Right VPN Tunnel for Daily Use
Turn on a reliable VPN service and you will often see a mysterious setting called “Split tunneling”. It decides whether all your Internet traffic goes through one VPN tunnel, or whether only selected traffic uses that secure tunnel while the rest keeps a normal connection.
In this guide, we will break down how a virtual private network and tunnel VPN actually work, what VPN tunneling strategy is behind a full tunnel VPN and a split tunnel VPN, and when each mode makes sense.
We will also look at real world warnings from security agencies, then show how VeePN helps you mix speed and VPN protection without exposing sensitive data on an open network.
What a VPN tunnel is in simple terms
Before choosing modes, it helps to understand what the VPN tunnel does.
A VPN connection between your device and a VPN server creates an encrypted VPN tunnel. Your device wraps all the data in an encrypted tunnel, sends it to the VPN, and only then it reaches websites and other Internet resources. In transit, tunneling encrypts your packets so anyone on the line sees only gibberish, not your logins or browsing.
Good VPN providers build this secure tunnel to reduce attacks on remote workers and home users. Security agencies like the NSA and CISA have even published joint guidance on choosing and hardening remote access VPNs because badly configured gateways were abused in real attacks.
So the tunnel is not just marketing talk. If VPN configuration is solid, it protects data transmitted over public Wi-Fi, untrusted networks, and other risky links.
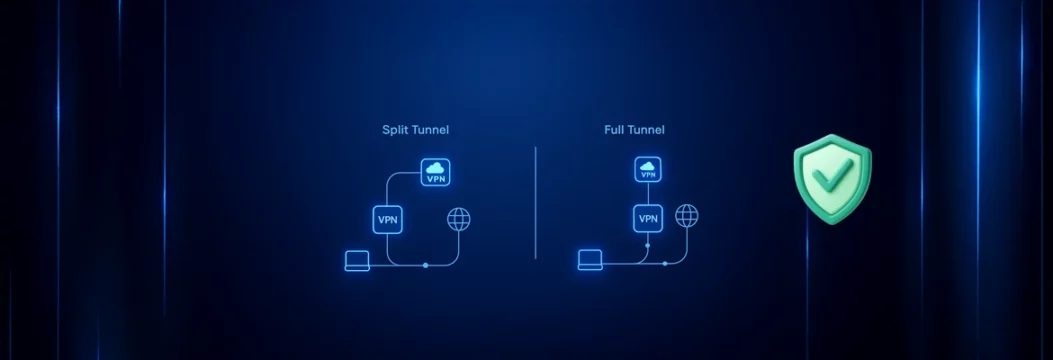
Split tunneling vs full tunneling in one look
How does Split tunneling vs full tunneling actually change your day to day Internet access? Here is the quick picture:
Full tunnel
In full tunnel mode, the VPN becomes the default mode for routing. All your traffic from the device goes into one encrypted VPN tunnel and exits through the VPN server. That gives you simple, broad VPN protection, especially useful on unsecured network links like hotel or airport Wi Fi.
Split tunneling
With split tunneling, only selected traffic uses the VPN. You might send your browser and online banking through the tunnel, while a game launcher or streaming app keeps direct Internet access over a regular Internet connection. In simple terms, split tunneling lets you decide which apps get the secure tunnel and which stick to a normal connection.
So let us see when full mode is worth the overhead and when a careful VPN split tunneling setup is fine.
When a full tunnel VPN is the safer default
Sometimes, simplicity and maximum security beat clever routing. That is where a full tunnel VPN shines.
A company VPN that links remote employees to a corporate network often uses full routing. Security standards and local government guidance for remote access stress that disabling split mode cuts the chance of leaks and keeps monitoring easier.
Where full tunnel still beats shortcuts
Here are cases where full tunnel or vs full tunnel VPN should win:
- Work on a corporate network. If your laptop reaches internal dashboards, HR tools, or file servers, a company VPN with full routing keeps that world behind one secure tunnel. Attack reports from CISA list misconfigured remote access VPNs among top issues that let attackers move laterally inside big networks. With all your Internet traffic forced through one gateway, it is harder for malware to sneak around your defenses.
- Public Wi-Fi and other untrusted networks. On public Wi-Fi or any public network, you do not control who sits between you and the router. A full setup protects all your traffic on that line instead of only a few apps. If the access point is malicious, it still sees just an encrypted stream to the VPN service, not which sites or Internet resources you visit.
- Non-technical users and shared devices. For some people, the safest setting is “turn VPN on and stop thinking about it”. With full routing, a VPN client covers browsers, background services, and other apps automatically. You do not have to remember which app you put inside the tunnel on each device individually.
The downside is that a full tunnel can slightly lower Internet speed, especially if the VPN server is far away or many people share the same gateway.
How split tunneling work and where it helps
Here, your VPN tunneling strategy is “tunnel for important things, direct line for the rest”. In most apps you can enable split tunneling in settings. From that point, the app uses rules to decide which Internet traffic goes through the VPN and which sticks with direct VPN access to the internet.
App-based split tunneling for everyday apps
The most user friendly option is app-based split tunneling. With it, you tell the VPN client which apps should always go through the tunnel. For example, you can protect your browser, work chat, and secure backup, while leaving a game or TV app on a regular Internet connection. This works well because it matches how operating systems and smart devices already show apps as separate icons, so you do not need to remember IP ranges.
App rules are handy when you want online gaming to stay fast while your browser still uses a tunnel VPN connection. You get privacy for your browser, speed for your game, and you do not have to toggle the whole VPN off every time you play.
Inverse split tunneling for a few exceptions
There is also inverse split tunneling, which flips the logic.
With inverse split tunneling, the VPN handles everything and you only list apps that may bypass it. This is safer than old school “everything direct except a few apps”, because your starting point is still close to complete protection. You can keep sensitive apps like online banking or work tools inside the encrypted tunnel, then let one streaming app or a local media player use direct Internet access if needed.
Dynamic split tunneling when your day keeps changing
Some setups support dynamic split tunneling.In that case, policies change with context. On a home network, your VPN might only route a few apps. On untrusted networks like café Wi Fi, the same device may flip to something closer to full tunnel until you disconnect. Dynamic rules can be great for remote employees, but they require careful VPN configuration. Otherwise, you might leave high risk apps outside the tunnel by accident when you switch locations.
URL-based split tunneling and why it is tricky
You build lists of websites that should bypass or always use the tunnel. This can be useful if one bank really hates VPNs and blocks VPN access, yet you want everything else secured. At the same time, routing by domain can create security risks if you accidentally send sensitive data to a login page over an unsecured network.
How to pick Split tunneling vs full tunneling in real life
The good news is that you do not need a degree to choose between split tunnel vs full. Let’s now think in the following scenarios:
- Working on a company VPN with sensitive systems. If you handle finance, HR, or internal admin tools on a company VPN, choose full tunnel VPN mode unless your security team clearly says otherwise. Guidance from NCSC, NIST, and others explicitly warns that split routing on remote endpoints can weaken protections and let attackers move between the device and internal file servers or apps.
- Home streaming, browsing, and casual gaming. For home use, a mix often works best. You can route streaming apps and online gaming through the tunnel to dodge throttling while keeping some local services on your local area network reachable over local network routes. VeePN’s own guides on how to change VPN location show how to unlock extra libraries without breaking your TV box or printer.
- Online banking and other sensitive apps. For online banking, tax accounts, and health portals, keep them entirely inside the VPN or entirely outside. Do not bounce these through multiple VPN providers or strange locations. One clean VPN tunnel to a nearby node or a clean direct line over HTTPS is better than a messy mix.
If you are unsure, start with full routing and only add split tunneling features for low risk apps that truly need better Internet speed.
Using split tunnel in VPN safely
If you decide to use split tunnel VPN at all, treat it as a power feature, not a toy. Here are a few simple habits that make VPN split tunneling safer:
- Start with a full tunnel and carve out carefully. Begin with everything in full tunnel mode. Then move low risk apps like streaming or game launchers to direct Internet access step by step. That is similar to using inverse split tunneling, where the tunnel is the standard and exceptions are rare. This mindset greatly lowers the chance that security risks creep in quietly.
- Protect high value traffic first. Anything that touches sensitive data, admin dashboards, or file servers should always use the tunnel. The same goes for password managers and secure email apps. Recent alerts from CISA about top misconfigurations show how quickly attackers exploit weak remote access setups to pivot inside networks.
- Watch for DNS and routing leaks. A bad split setup can send DNS lookups out over the ISP while content flows through the VPN. That exposes where you go online, even with a tunnel. VeePN’s guides on DNS leak protection and our online DNS leak test explain how to check if queries stay inside the tunnel or escape through your ISP.
- Test on different operating systems and smart devices. Different operating systems handle routes differently, and some smart devices do not support split mode at all. Before trusting a setup, test it on phones, laptops, and streaming boxes to see how tunneling works in practice.
Used this way, split tunneling vs full tunneling becomes a conscious choice instead of a random toggle.
Why VeePN fits both Split tunneling vs full tunneling styles
Now to the practical part. How does VeePN help when you want both strong VPN protection and flexible routing?
- Powerful encryption for a secure tunnel. VeePN uses strong, modern encryption so your VPN tunnel acts as a real secure tunnel, not a cosmetic feature. Even if you use split routing, anything inside that encrypted tunnel stays unreadable on public network links and other risky routes.
- IP masking and easy location changes. VeePN hides your real IP address behind its servers and lets you quickly switch locations. That is useful in full mode to keep all your Internet traffic away from local snoops, and in split mode when you only need certain apps to appear in another country, as described in VeePN’s tutorial on how to change VPN location.
- Kill Switch and DNS leak protection. If the VPN connection drops, the Kill Switch cuts traffic instead of silently falling back to an open network. Combined with VeePN’s DNS leak shield, this stops other traffic or lookups from leaving the tunnel by mistake, which is critical when you use split tunneling and background services keep talking to the internet.
- 2600+ servers for speed and local resources. With thousands of servers worldwide, you can pick nearby locations to keep Internet speed high even with a full tunnel. You can also choose specific regions for streaming or gaming while still reaching local resources on your local network using smart routing or router level installs.
- No Logs policy. VeePN follows a strict No Logs approach, so your Internet traffic in the tunnel is not turned into long term records. That is important no matter which VPN tunneling strategy you pick.
Put simply, VeePN gives you the tools to run a strict full tunnel VPN when you need it and a flexible, safer split tunneling setup when speed and convenience matter more.
FAQ
With a full tunnel, the VPN carries all your traffic through one VPN tunnel to a remote server. With split tunneling, only selected traffic goes through the tunnel and other traffic uses a direct route. Full mode is simpler and safer on untrusted networks, while split mode trades some protection for speed and flexibility. Discover more in this article.
The main benefit of split tunneling is control. You can keep sensitive apps and work tools inside the secure tunnel, while giving games or streaming direct Internet access to reduce lag. It also helps when you need secure access to office apps but still want local services on your home network to work like usual. Discover more in this article.
If you are on public Wi-Fi or inside a corporate network, it is usually safer to keep split tunneling off and use a full tunnel. At home, you can turn it on for low risk tasks like online gaming or streaming, as long as important accounts and sensitive data stay in the tunnel. The safe rule is to start with full routing, then enable splits only where you really need them. Discover more in this article.
Used well, split tunneling can actually improve perceived Internet speed, because less traffic goes through the VPN, freeing capacity for what matters most. If the VPN server is slow, both full and split modes will feel heavy, but splitting lets heavy, low risk apps use a normal connection instead of the tunnel. The key is to send only what truly needs VPN protection through the encrypted path. Discover more in this article.
VeePN is freedom
Download VeePN Client for All Platforms
Enjoy a smooth VPN experience anywhere, anytime. No matter the device you have — phone or laptop, tablet or router — VeePN’s next-gen data protection and ultra-fast speeds will cover all of them.
Download for PC Download for Mac IOS and Android App
IOS and Android App
Want secure browsing while reading this?
See the difference for yourself - Try VeePN PRO for 3-days for $1, no risk, no pressure.
Start My $1 TrialThen VeePN PRO 1-year plan