Global Payments Fraud: Analyzing the Latest Trends in Credit Card Theft
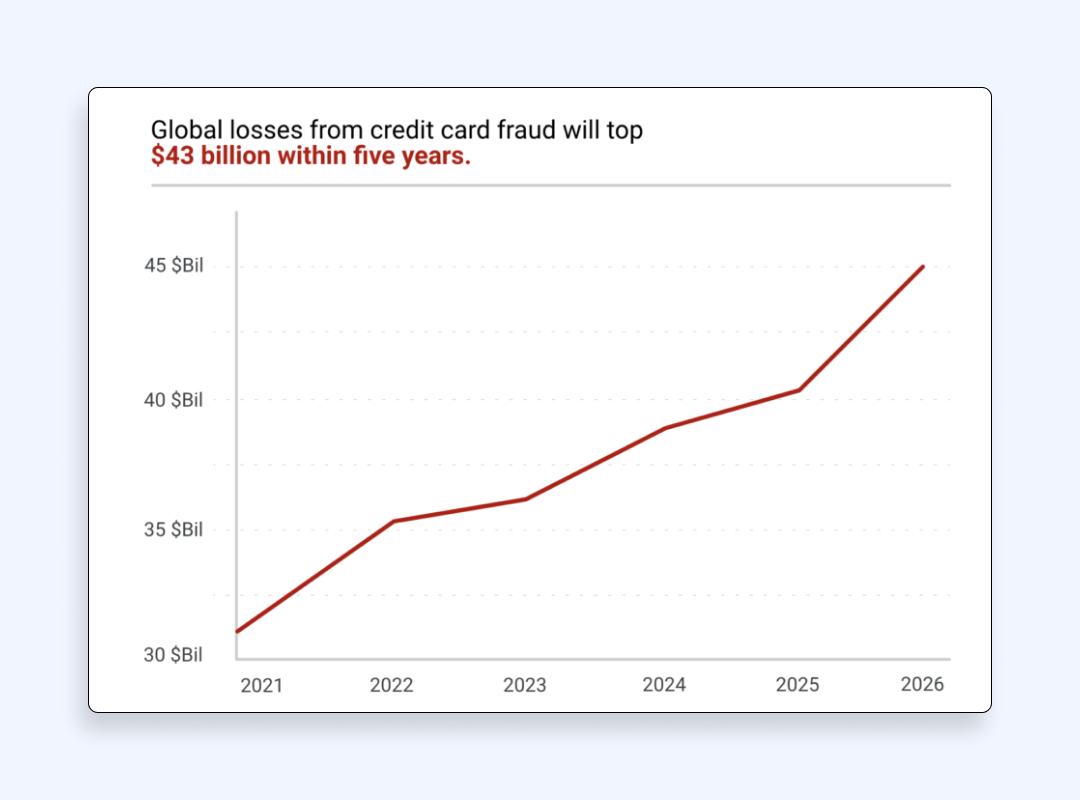
Navigating the world of online payments today is like stepping into a digital minefield — one wrong move, and your finances could be left in shambles. Fraudsters are constantly setting more and more sophisticated traps, waiting for the moment when an unsuspecting consumer missteps. The harsh reality? Credit card crime is skyrocketing, with global losses expected to reach $43 billion by 2026.
From advanced phishing scams and card skimming techniques to stolen credit card details on the dark web marketplaces, payment fraud is evolving rapidly. While financial institutions and cybersecurity firms are racing to stay ahead, cybercriminals are equally innovative, leveraging AI-driven attacks and social engineering tactics to exploit vulnerabilities.
In this article, we’ll dissect the latest trends in credit card theft, expose the tactics criminals use, and most importantly, arm you with the knowledge to step safely through the treacherous woods of digital transactions. Because in today’s world, protecting your financial information isn’t just an option, it’s a necessity.

Fraud explosions hit hard (and will only get worse)
The current situation with online payment fraud attacks is already concerning. The number of attempts to steal money from credit cards is growing by 46% year-over-year. Provided that these estimates are accurate, we can observe a 4.5x increase in payment scams number over the last 15 years.
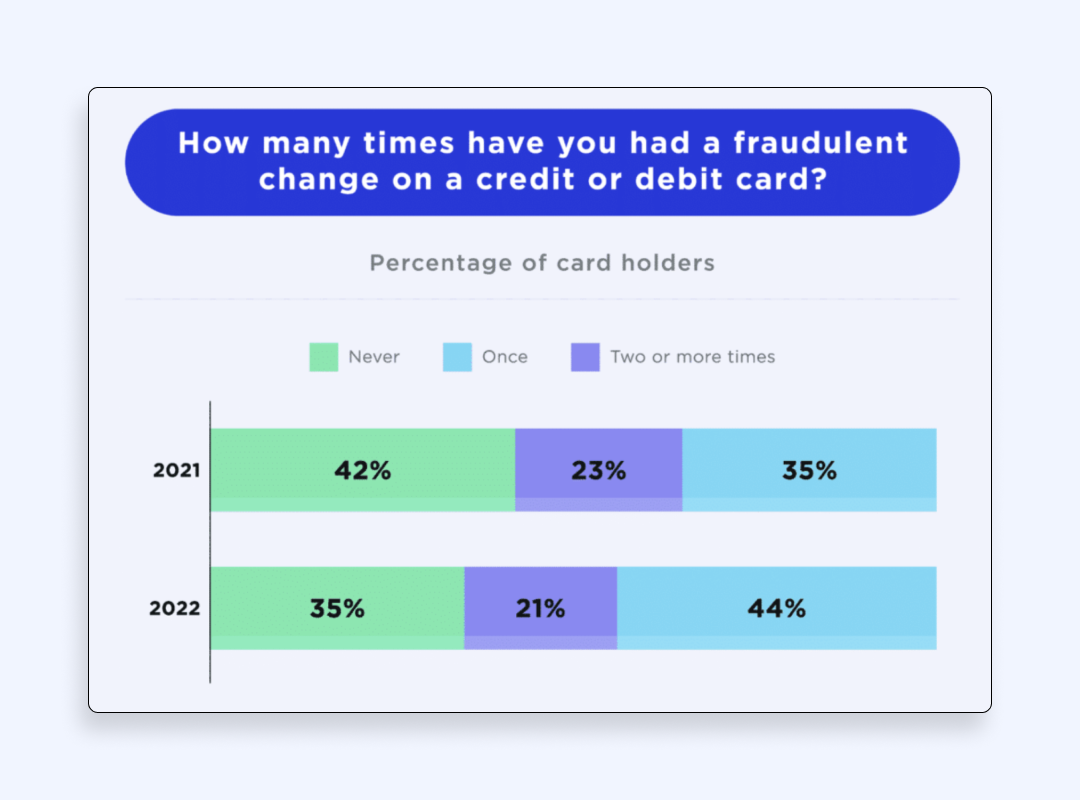
Under these circumstances, around 20% of the global population has suffered a financial loss because of payment scams at least twice. Such a blazing-fast uptick in the number of credit card scams is a big canary in the coal mine. The global financial infrastructure is going to suffer a deadly strike in the future, so it has to take action now.
However, while we are discussing valuable insights into the global situation, credit card fraud statistics related to the most important players such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and the European Union require separate coverage.
The United States
Speaking about the incidence of payment fraud in the US, it’s crucial to remember that around 46% of all payment scams happen in the United States which is equal to $12.5 billion. Numbers-wise, every 14 seconds someone in the US falls victim to a credit card scam! Taking this data into account, we can say that US consumers face serious risks with payment security.
The UK and Europe
As for the United Kingdom and the European Union, the UK appears the leading country regarding payment frauds. Actually, every 123 out of 1,000 UK residents are affected by payment frauds.
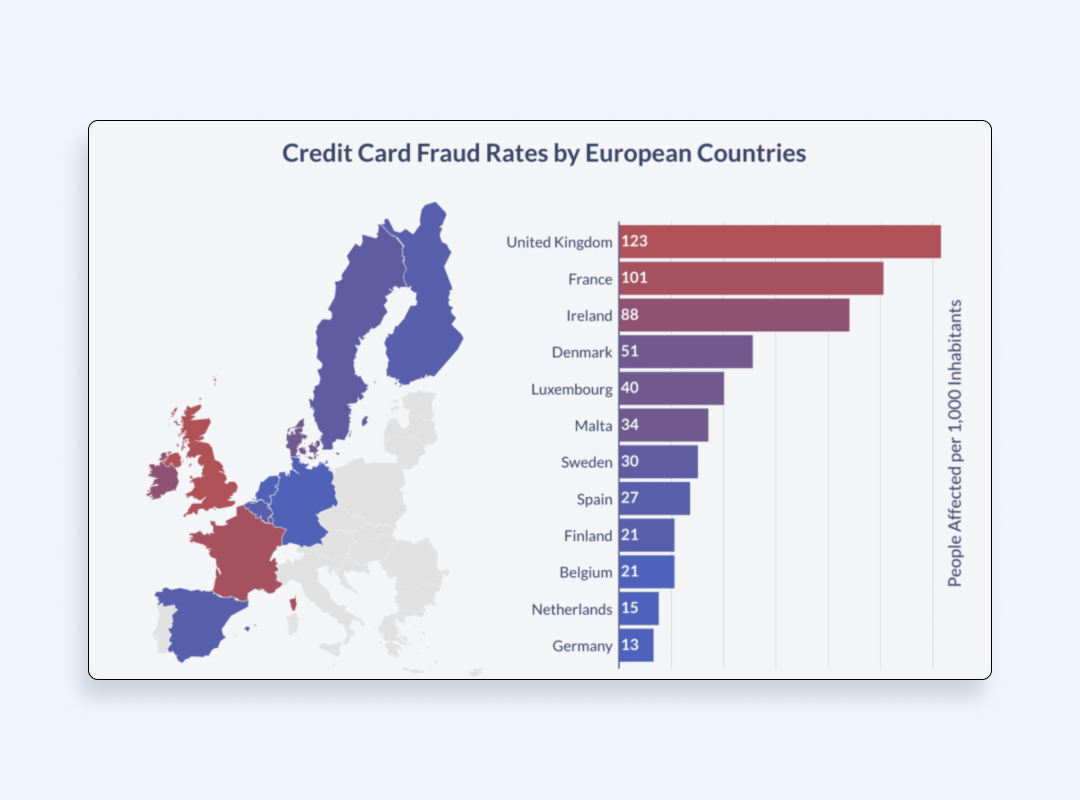
At the same time, two-thirds of German and 85% of Swiss e-commerce businesses report recurrent problems with payment scams targeted against their customers. Overall, the UK and Europe appear in a relatively advantageous position in comparison with the US, but the above-mentioned threats indicate they are in no lesser danger.
What do we see now? The biggest financial systems suffer from serious security threats that keep evolving. Let’s explore them in detail, so you can recognize these minefields and avoid stepping on them.
Dozens of scam mines waiting to be stepped on
Since payment frauds are so common, it’s natural to expect that there are numerous types of them. Let’s review the most widespread payment fraud trends you need to be aware of to keep your personal information and money secure:

Application-to-Person (A2P)
An A2P fraud involves the use of an application that sends a phishing text as SMS, email, or message. This text may contain a link leading to your data leakage or installation of spyware. That is why you have to be careful with suspicious messages offering you a prize/discount, urging you to share your personal information, or attempting to represent someone you know.
Toll and phone calls
Toll fraud happens when scammers gain unauthorized access to telecommunications services, typically through cloud-based systems. Unlike A2P fraud, which involves sending messages, toll fraud relies on phone calls to generate revenue.
In the same vein, phone call frauds also use telecommunications to target you with social engineering tactics. Scammers may attempt to force you to share your personal information by saying they’re government officials or bank support agents and there is an issue with your account or documents. By making you feel worried and urged, the scammers aim to make you act without thinking about the consequences and voluntarily share your sensitive information.
Likewise, fraudsters may lure you into a trap by saying you have won the prize or a big discount and to claim your reward you need to share your banking details. Remember, there is no such thing as a free lunch. Our ultimate recommendation is to hang up on any conversations that sound odd to you. If it was for real, people that contacted you will understand. If it were scammers, they had gone with nothing.
Synthetic identity theft
Synthetic identity theft is a form of fraud in which criminals combine real and fabricated personal data to create a new, fictitious identity used for illegal financial activities. Fraudsters use a mix of real and fake details to create an impression that a person behind a fake profile is real and authorized to make financial decisions. For instance, scammers can use your personal information they have and forge the rest of the missing details to get a loan on your behalf.
Account takeover (ATO)
This fraud method is as simple as it sounds. A cybercriminal steals your login credentials for your banking app and transfers all your funds to another account. This method usually works together with various phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. Brute-force cracking of your password is also possible, which means you have to come up with complex hard-to-crack passwords for all your banking applications.
AI-driven scams
With artificial intelligence (AI) software being in vogue, it’s no wonder scammers and hackers won’t miss an opportunity to use it for their malicious intentions. The scale of how AI becomes a weapon in the wrong hands is impressive, indeed.
Arup, a British-Hong Kong design company, suffered a loss of $25 million because of falling into a trap involving deepfake voice messages and images that made the company’s employees believe they shared sensitive information with the company’s top executives. Even though the company is not ready to disclose the details of the incident, they confirmed the attackers used AI-created fake voice messages and images.
Even YouTube happened to be a target for AI-driven phishing attacks. YouTube creators are lured into sharing their sensitive information with a deepfake of the company’s CEO, Neal Mohan. YouTube creators confirmed they received email messages with a video from Mohan introducing a “new monetization” policy or instructions to download a malicious file attached.
On top of that, AI-powered scams have become so widespread and easy-to-craft that the entire Fraud-as-a-Service (FaaS) platforms start appearing on the dark web. Users with little to no experience in generating fake media depicting a particular person can easily use such a toolkit for deception of their victims. Since it’s so easy, such a practice gets a rapid-fire ascent of attention from individuals looking for easy money earned with a dirty, tricky job.
Card-not-Present fraud
Card-not-present (CNP) scams are the most common attacks aiming to steal your money online, so we need to dive a little deeper into the subject. A CNP attack is a payment fraud that steals money from a user’s credit card without even having a physical contact with it.
There are different cases, in which such an attack can happen:
- Online shopping
- Phone orders
- Delivery/shipping orders
- Recurring payments such as subscriptions
- Mobile/digital wallet payments
- Virtual point-of-sale terminal payments
- Orders via fax
In all these and other similar cases, cybercriminals get access to your credit card information such as number, expiration date, CVV code, PIN code, and so on. With this information, scammers can make purchases and transfer funds from your card or sell it on the dark web. So, how do they steal your card details? There are several ways:
💥Social engineering. Social engineering uses deceptive tactics that trick individuals into sharing sensitive information or granting access to restricted systems. These methods encompass a range of strategies, including phishing, spear phishing, baiting, pretexting, tailgating, and quid pro quo attacks.
💥Spyware. Scammers use the aforementioned social engineering tactics to spread malware that will spy on you and collect all your sensitive information without you knowing.
💥Data leaks. No website or online service is secure, so when a data breach occurs, the information you submitted to this or that site will get into scammers’ dirty hands. The outcome is obvious: you risk losing all your money from your banking cards.
💥Public WiFi networks. Since public WiFi hotspots are commonly unsecured, they are a breeding ground for scammers and hackers waiting for unsuspecting users. When you use a public WiFi without a reliable protection such as VeePN, you risk exposing your data to a stranger sitting at the next table.
💥Card skimming. Scammers install covert skimming devices on ATMs and point-of-sale (POS) terminals to secretly retrieve data from a card’s magnetic strip each time it’s used.
💥Interception of NFC signal. It’s one of the trickiest methods to get your card data for a CNP attack. Many cards as well as mobile devices contain a near-field communication (NFC) chip we use for making contactless payments when you don’t need a physical credit card to get applied to a POS terminal. With the help of the NFCGate app, fraudsters intercept a signal from your mobile device at the moment of payment and get all the necessary data. In such a way, even such secure payment methods as ApplePay may not protect you against this attack as your device will serve as an NFC signal “relay” that transmits all transaction data.
Triangulation fraud
This type of fraud is actually a version of a CNP attack. Triangulation fraud typically involves three key players, which are the customer, the fraudster, and the merchant. The process usually goes like this:
- the fraudster sets up a bogus online marketplace, advertising products at enticingly low prices.
- A deal-seeking customer stumbles upon the listing and places an order, unknowingly handing over their personal and payment details.
- The fraudster then uses this information to charge the victim’s card.
Next, the fraudster uses a different cardholder’s payment details to order the same item from a legitimate merchant, who ships the product to the unsuspecting customer. Everything appears fine until the rightful cardholder spots the unauthorized charge for an item they never purchased — leading to a chargeback that hits the merchant.
Cross-border payment scams
In the globalized world, cross-border payments aren’t something exotic but definitely a low-hanging fruit for scammers. Since security measures and regulations differ across countries, fraudsters use these differences to their advantage.
Gift card scams
This type of scas is also on the rise because gift cards are common and easy to resell. Scammers use various techniques to steal funds from gift cards, ranging from tampering with physical cards to creating bots that guess valid card numbers. This method has become extremely widespread, so we recommend you keep being vigilant when you purchase Steam, Amazon, or any other gift cards or vouchers.
The list of online payment mines you can accidentally step on is obviously long but unfortunately not exhaustive. On the upside, we have a wide range of ways to defuse them!
How threats get defused
We’re going to put digital payment fraud prevention under the microscope, but before we do this, we would like to remind you that we need to focus on the US and European financial systems again because they’ve made the most tangible progress in countering payment scams online.

The US
The process of payment fraud investigation/prevention appears to be far more complicated than you may imagine and definitely is worth another deep-dive article. But for a basic understanding of how it works in the United States, be welcome to learn about the process that is the following:
1. Investigation process
- Initial detection: Automated fraud detection systems flag unusual transactions in real time. Issuers then contact cardholders to verify suspicious charges.
- Data analysis: Specialized teams review transaction data, identifying patterns that suggest organized fraud. This could include multiple purchases across different geographies or high-value orders placed in quick succession.
- Collaboration: Banks, payment processors, merchants, and federal agencies such as the FBI and Secret Service share insights on emerging threats to streamline investigations and improve response times.
2. Preventative measures
- Card security features: Biometric authentication and tokenization significantly reduce the risk of data theft and illicit card cloning.
- Merchant compliance: Retailers follow Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) guidelines to protect consumer data, including secure network protocols and routine vulnerability scans.
- Proactive monitoring: Banks and payment networks use advanced AI-driven systems to detect anomalies and proactively block suspicious activity before it escalates.
3. Consumer education & support
- Awareness campaigns: Financial institutions and consumer advocacy groups encourage users to regularly check statements and report unauthorized transactions.
- Liability protection: Under federal law (such as the Fair Credit Billing Act), cardholders in the US typically face minimal liability for confirmed fraudulent transactions, incentivizing prompt reporting.
- Dispute resolution: Once suspicious activity is reported, the issuing bank investigates the claim, refunds legitimate disputes, and may pursue legal action against fraudsters in cooperation with law enforcement.
Europe
While the fundamental challenges of tackling fraud are universal, European regulators and institutions use certain region-specific measures and frameworks to protect consumers and businesses.
1. Investigation framework
- Cross-border coordination: European authorities such as Europol and national-level financial investigation units cooperate to track criminal activity across multiple jurisdictions.
- Regulatory oversight: Entities like the European Banking Authority (EBA) and European Central Bank (ECB) set directives and guidelines for banks and payment providers, encouraging unified anti-fraud protocols and reporting standards.
- Centralized data sharing: Common databases and intelligence networks help detect large-scale fraud patterns, providing timely alerts to financial institutions about emerging threats.
2. Preventative measures
- Strong customer authentication (SCA): Under the Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2), cardholders are frequently required to authenticate transactions using two or more factors such as one-time passwords or biometric data.
- EMV & contactless protections: European markets have widely adopted Europay, Mastercard, and Visa (EMV) chip technology, which helps reduce counterfeit fraud. Contactless payments also incorporate transaction caps and random PIN checks to minimize abuse.
- Data protection requirements: GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) mandates rigorous data handling and breach notification protocols, limiting unauthorized access to sensitive cardholder information.
3. Consumer education & support
- Public awareness: Regulators and consumer protection agencies run campaigns promoting safe online shopping habits, such as using secure connections and monitoring accounts for suspicious activity.
- Dispute resolution processes: European banks typically offer transparent chargeback procedures. If a transaction is disputed and confirmed fraudulent, the cardholder is protected from liability under EU consumer laws.
- Ongoing initiatives: Joint working groups, involving law enforcement and financial institutions, continuously refine anti-fraud strategies by pooling knowledge and sharing best practices across the continent.
We’ve covered how fraud investigations take place both in the United States and Europe. And now, it’s time to talk about the most effective methods of preventing payment scams online.
The best payment scams defusing methods
The world is facing a serious threat of turning its financial system into a honeypot for scammers and fraudsters. At the same time, there are numerous ways that say “no-no, you shall not pass” to malicious actors . Here are the most effective payment fraud detection techniques:

✂️Tokenization. It replaces your card number and other details with random symbols that comprise a so-called token attached to your card. Every single time you make a transaction, a merchant sends a request to your payment system to create a unique token assigned to your card. As a result, you can make payments online without exposing your data to third parties.
✂️Rule-based security. Payment systems often include a set of rules and patterns that signify authorized transactions. When such a pattern is broken, it means that some suspicious activity is taking place, and the security team can take immediate action to prevent attempts of unauthorized access. Also, rule-based security may come hand in hand with AI-driven behavioral analytics to detect odd and suspicious actions such as multiple login attempts, simultaneous transactions made from different locations, or authorization from unknown devices.
✂️Multi-factor authentication (MFA). This simple yet effective method requires you to submit different types of verification data such as password, biometric data, one-time password, or official document scans to access your banking app and use cards for transactions.
✂️Device fingerprinting. When you create an account in a particular banking app, you associate your profile with certain devices you use. In case a transaction takes place from a device other than you’ve selected, it will be blocked or additional verification steps must be taken.
Needless to say, these defusing methods work on the side of service providers, merchants, financial institutions, and government agencies. But how can you recognize you’re one leg on a payment scam mine? Keep on reading to explore the most common signs of online payment frauds!
Signs you’ve stepped on a payment fraud mine
If you observe at least one of these signs, it’s high time to pull yourself by the sleeve and take action toward protecting your personal and financial data. Watch out for such red flags as:

💣Unauthorized transactions on your bank or credit card statement. If you notice charges you don’t recognize, especially for unusual amounts or merchants you’ve never used, it could be a sign of fraud. Scammers often start with small “test” transactions before making larger purchases. Always review your statements carefully and report anything suspicious immediately.
💣Unexpected declined payments despite sufficient funds. If your card is declined even though you have money in your account, it may indicate fraud prevention measures or that your account has been compromised. Banks sometimes freeze accounts after detecting unusual activity. Contact your bank to confirm if your card has been flagged for security reasons.
💣Fraud alerts or suspicious transaction notifications from your bank. Many banks and credit card issuers send real-time alerts for transactions that appear unusual. If you receive an alert for a purchase you didn’t make, it’s a bad sign that someone else may be using your payment details. Respond to fraud alerts quickly to prevent further unauthorized charges.
💣Unauthorized changes to your account details (email, phone number, password). If you receive an email confirming changes you didn’t make, such as a password reset or updated contact information, your account may have been hacked. Cybercriminals often update these details to lock you out of your own account. Secure your account by resetting passwords and enabling two-factor authentication (2FA).
💣Unexpected withdrawals or money transfers from your account. If money disappears from your checking or savings account without your authorization, it’s a serious sign of fraud. Criminals might use your banking details to make wire transfers or withdraw cash. Immediately contact your bank to dispute the transaction and secure your funds.
💣Fake invoices or double charges for purchases. Receiving a bill for a product or service you never ordered is a classic fraud tactic. Similarly, being charged twice for the same purchase without a refund could indicate a billing error or scam. Always verify invoices and check with the merchant before making a payment.
💣Suspicious emails, texts, or calls asking for payment details. Scammers often pose as banks, payment services, or well-known companies, claiming there’s an issue with your account. They may send phishing emails with fake links designed to steal your login credentials. Never provide sensitive information via email or text and contact the company directly to verify.
💣Sudden drop in your credit score due to unauthorized accounts. If your credit score drops unexpectedly, someone may have opened credit lines in your name. Fraudsters use stolen personal information to take out loans or apply for credit cards. Check your credit report regularly to spot unfamiliar accounts and report identity theft immediately.
💣Subscription or membership charges you didn’t sign up for. Fraudsters sometimes enroll stolen card details in recurring subscriptions for streaming services, software, or memberships. If you see charges for services you never subscribed to, it could indicate unauthorized use of your payment information. Review and cancel any unknown subscriptions immediately.
How to protect yourself from online payment scams
Leaking your personal information online is the main factor in stepping on a payment fraud landmine. Sharing your sensitive data via social media, submitting it to a poorly secured site, just using a public WiFi hotspot, or even appearing in the wrong place at the wrong time can put your Internet privacy and your savings at risk. Additionally, trackers, spyware, and advertisers are waiting for your financial data online, so protecting one isn’t just a nice-to-have thing but a necessity dictated by the harsh reality which, as you can see, is going to get only worse.
There is no better way to protect yourself than to use a virtual private network (VPN). When you turn on a VPN app, all your Internet traffic goes through an isolated “tunnel” where it gets encrypted and turned into a bunch of unreadable gibberish. Then, your traffic passes through a remote server and finally reaches its destination. As a result, you can prevent tracking of your online activities and hide your IP address, so that nobody can detect your real location.
Nevertheless, we want to warn you against using free VPN applications as they don’t provide reliable encryption standards and actually collect your personal information for commercial purposes which actually negates the entire point of using a VPN app. To truly protect your identity and financial information online, consider using VeePN, a premium VPN service with various security features and advanced benefits:
🛡️Military-grade encryption. VeePN uses AES 256-bit encryption which is considered the most secure standard so far. Even if scammers manage to catch your Internet traffic on the go, they won’t be able to interpret the encrypted data and use it to rob your credit cards.
🛡️Expanded network of servers. With 2,500+ servers across 89 countries, you can be sure your financial information is always protected wherever you go or make payments online. Also, such a huge network of servers optimizes your connection speeds as our servers never get overcrowded.
🛡️Double VPN. If you need to add an extra layer of security to your online payments, this feature can help. When you enable a double VPN, it means your traffic passes through two remote servers and gets encrypted twice. Deciphering such a long string of random symbols is impossible.
🛡️Device compatibility. VeePN is compatible with a wide range of devices, so your iOS, Android, macOS, Windows, and other devices can be secure with just one subscription.
🛡️Breach Alert. In case your personal information gets leaked and appears in scam databases, this tool will send you an instant notification, and you’ll have time to take preventive action.
Equipped with such features as Alternative ID and Anonymous Email, VeePN can be your ideal protection tool for payments online. Get VeePN today and enjoy a 30-day money-back guarantee!
FAQ
The largest source of credit card fraud today stems from card-not-present transactions, particularly in online purchases. Data breaches that expose consumer card details also play a significant role, allowing criminals to buy and sell stolen information easily on the dark web.
Exact statistics on how much credit card fraud is actually caught can vary, and there is no single global figure. However, financial institutions and card networks invest heavily in fraud detection systems, and some estimates suggest that a significant portion — often over half — of fraudulent attempts are detected before customers are charged. That said, the percentage of criminals ultimately identified and prosecuted is believed to be much lower, due to challenges in tracing and coordinating investigations across jurisdictions.
Around 20% of all credit cards have been attacked at least twice. The global losses from online card frauds are likely to grow up to $43 billion, these losses will be 4.5 times bigger than 15 years ago. Overall, the situation with payment scams gets worse each year, which is why it’s essential to be careful with making transactions online.
VeePN is freedom
Download VeePN Client for All Platforms
Enjoy a smooth VPN experience anywhere, anytime. No matter the device you have — phone or laptop, tablet or router — VeePN’s next-gen data protection and ultra-fast speeds will cover all of them.
Download for PC Download for Mac IOS and Android App
IOS and Android App
Want secure browsing while reading this?
See the difference for yourself - Try VeePN PRO for 3-days for $1, no risk, no pressure.
Start My $1 TrialThen VeePN PRO 1-year plan