What Is a VPN Tunnel and How It Works
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) and tunnels are two pieces of the same cybersecurity puzzle. Although certain of us can make the two interchangeable, VPN does not always imply a tunnel and vice versa. It is not quite that simple so we shall proceed with what a VPN tunnel is and how does the process of tunneling occur.
An effective VPN does not save on security measures. VeePN provides an encryption of 256-bit AES that cannot be cracked, more than 2500 secure servers, and double VPN to provide an additional level of protection. In the case that your privacy on the internet is important, it is important to secure your connection using the appropriate tools.. Sign up for VeePN today to see for yourself.
What is tunneling?
In networking, tunneling is an encryption and encapsulation process used to securely send private communications across the internet or other public network. Tunneled traffic sent as encrypted packets gets encapsulated with routing information so your Internet traffic can move securely through a VPN server and arrive at its intended destination.
VPN tunnel
VPNs involve tunneling to offer you a secure connection between the information requesting device and the web site or server you are browsing. Since the VPN tunnel hides your activity and masks the user’s IP address, even the government or your ISP will not be able to know what you are browsing.
What is a VPN tunnel?
A VPN tunnel is a secure and encrypted connection between your gadget and a safe server. The operation enables confidential messages to pass through the internet and other open networks without any danger. Since a VPN will keep your traffic undetected since it is encrypted in a tunnel, it is the best way to navigate the web in a secure and confidential manner.
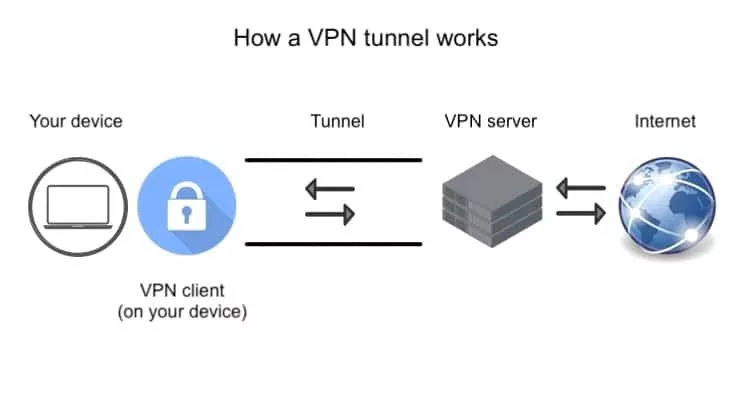
How does a VPN tunnel work?
VPN tunnels work in several stages. First, you must encrypt data at the source and send the protected packets to a secure server where they undergo decryption. Then your encrypted traffic is sent to its destination, and the VPN server receives the reply before forwarding it back to you.Here, it works again using Internet protocol security, and continued information stored in an encrypted message is sent back through an encrypted protocol to your device and decrypted.
Let’s discuss the concepts of VPN tunneling in more detail.
Data encryption
One of the initial and most significant processes in the VPN tunneling process is encryption. In the absence of high-level encryption, your Data packets and network traffic can be easily intercepted by anyone who has the ability and software to decode your traffic.
Using a tunnel, an encrypted connection is made between your device and a secure server in the possession of your VPN provider. It is only that server that can decrypt your data, and it must do so in order to send you to the right destination. All return traffic also undergoes encryption — this time at the server — before returning to your device.
Apparently, your tunneling requires a powerful encryption technique to ensure its security. Ideally, when choosing and setting up a VPN app, you should use the best quality of encryption that works smoothly across various operating systems.
Optimal location
Choosing the ideal server for your VPN connection is crucial to performance. If you select a location that’s far from where you are, the extended distance your traffic must travel could inhibit speed. Therefore, choosing a server that’s close to home is ideal when performance matters.
VeePN offers over 2600 locations to choose from, which means you can select a server that suits your browsing needs. If you need to bypass firewalls or the geo-blocking tactics of a streaming service or another site, a wide range of virtual servers makes fooling the filters easy.
VeePN has more than 2600 locations to be selected and that is you can select a server that best fits with your browsing purpose. In case you want to circumvent the geo-blocking measures of a streaming platform or any other website, with a large pool of virtual servers, it is very simple to trick the filters.
On top of that, VeePN’s optimal server setting allows you to quickly connect to a location that will deliver the best performance, which means you don’t need to waste time finding the best connection.
Double VPN
Using a double VPN — or VPN chain — adds an extra layer of security to your connection. Instead of tunneling to one secure server, your traffic also routes to a second location and undergoes additional encryption. Adding another step to the journey can decrease speed, but relying on a secure VPN tunnel may be worthwhile in situations where you need absolute protection.
No logs
If your VPN provider logs traffic that arrives at its secure servers, the service isn’t safe to use. Some countries have strict laws that require companies to hand over any information when requested. If your VPN provider keeps logs, your private data could end up in the hands of the nations in which its servers reside.
To truly preserve your online anonymity, you should only opt for a VPN service that has a no-log policy.
Kill switch
A kill switch is a fundamental part of any safe and reliable VPN. Connection issues and dropouts can leave your traffic exposed. However, when you have a kill switch active, your VPN software automatically disconnects all devices when necessary until it can re-establish a safe, encrypted tunnel to the server.
VPN tunneling protocols
Although we have established the mechanism of tunnels, without a protocol, a VPN would not work. Did you notice that there is a list of available protocols to select some VPN provider? Now, we should speak about the subject matter in greater detail.
What is a VPN tunneling protocol?
A tunneling protocol is the software used by a VPN to secure your connection through strong encryption protocols and perform its intended function. Different protocols exist, and each one offers varying features relating to encryption, speed, and general performance.
What are the main types of VPN tunneling protocols?
Here are some of the top VPN tunneling protocols, including standards like secure socket tunneling protocol:
- OpenVPN
- IKEv2
- L2TP/IPSec
- Wireguard
OpenVPN is an open-source VPN protocol with the ability to provide 256-bit encryption. Internet key exchange version (IKEv2) is more of an authentication protocol rather than an actual standalone protocol. The L2TP/IPSec is also 256-bit encrypted but is potentially becoming obsolete, much like the older point tunneling protocol pptp.
Wireguard is a fairly recent open-source VPN protocol which utilizes current cryptography to safeguard your connection and offer high-performance. VeePN also supports Wireguard, as well as OpenVPN, and IKEv2, and therefore, you have the choice of the protocol that fits your requirements.
Split tunneling
VPN split tunneling gives you more control over your traffic and connection. If you don’t need all of your outgoing information encrypted, splitting your data into separate tunnels may be ideal.
What is split tunneling?
Split tunneling can be used to tunnel selected traffic over an encrypted VPN tunnel and use the remainder of the information to be sent to the open web. It will be desirable to send apps that contain sensitive information to the VPN and other less sensitive traffic to the unencrypted connection when using the feature.
Do you need split tunneling?
Split tunneling is ideal for anyone who wants to encrypt certain information on desktops or mobile devices but preserve Internet speed when dealing with less-sensitive data. For example, you could choose to encrypt your browsing activity while leaving your online games or other services open so increased latency doesn’t affect performance.
If you’d prefer to have all of your traffic treated the same — either encrypted or not — split tunneling isn’t necessary.
Everyone should use a VPN tunnel
When you connect to the Internet using an unsecured connection, you are putting your traffic at risk of being trailed by hackers, government agencies, network managers and your Internet Services providers. Thus, encryption matters, and a decent VPN service, such as VeePN, will make your browsing behavior and private data confidential.
FAQ
Is tunneling the same as VPN?
As a rule, it is the process of tunneling that ensures the connection and traffic is encrypted, and VPN is the Virtual Private Network itself.
What do you need for a VPN tunnel?
All you need to create a secure tunnel is a good VPN service provider and the appropriate software on your device.
Is VPN tunneling illegal?
VPN tunneling isn’t illegal in most places. Generally, you have the right to secure your connection and protect your private data whenever you see fit.
How many VPN tunnels can you have?
Depending on the service you are using and the features of software you are given, split VPN tunnels will have varying numbers of split VPN tunnels that you are allowed to use simultaneously.
VeePN is freedom
Download VeePN Client for All Platforms
Enjoy a smooth VPN experience anywhere, anytime. No matter the device you have — phone or laptop, tablet or router — VeePN’s next-gen data protection and ultra-fast speeds will cover all of them.
Download for PC Download for Mac IOS and Android App
IOS and Android App
Want secure browsing while reading this?
See the difference for yourself - Try VeePN PRO for 3-days for $1, no risk, no pressure.
Start My $1 TrialThen VeePN PRO 1-year plan