Phishing vs. Smishing: What Are the Most Common Scams and How to Prevent Them?
Imagine you’ve received a message or an email from a bank asking you to confirm information about your personal account. All you need to do is click on a link, fill out a short form, and you’re done. Not a big deal, right? Well, here is the thing. Very likely, the notification wasn’t sent by your bank, but by someone wishing to steal your private data. In other words, you’ve just got hooked by a phishing or smishing scam.
Phishing and smishing are some of the most common and dangerous scam types putting your cybersecurity at enormous risk. But what is the difference between phishing and smishing? And what can you do to fight them? Keep reading this post to find out.
What is phishing?
Let’s start with the essentials and provide the definition of phishing attack.
Phishing is a widespread type of social engineering cyber attack striving to get people’s personal data and use it to steal money or spread malware. A phishing attack often appears as a compelling email or another type of message. It pretends to be sent by a trusted company or website. However, the actual sender is a hacker, and the message is fake.
In most cases, email phishing doesn’t work like brutal cyber attacks. Instead, it plays with people’s feelings and attempts to catch them off guard. When you see a message claiming that something is wrong with your account, password, or credit card, you will likely get scared, concerned, or, at least, confused. And that’s where you run the risk of getting trapped.
Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2021 reports phishing to be the most widespread online scam. Moreover, the threat is equally high for individuals and businesses. So how to spot a scam and avoid getting caught in phishing nets? First and foremost, it’s crucial to understand the attack’s specifics so that you can distinguish it from a legitimate email. Here are some of the most typical phishing signs to look out for:
- Unexpected or unusual alerts and requests
- Notifications requiring to act immediately
- Emails requesting personal data, like payment details, account number, or credentials
- Suspicious links, attachments, or CTAs
- Grammar mistakes, spelling errors, or low-quality images
Different types of phishing
Phishing is usually associated with emails aiming to obtain personal data or other sensitive information. However, today, there are various forms and types of this scam. Let’s look at the most common ones:
- Spear phishing targets specific individuals, companies, or businesses, providing fake information to provoke their interest or concern. Nowadays, spear phishing is one of the fastest-growing security threats. 65% of cyber criminals focus on this attack vector.
- Whaling is a specific type of spear phishing that targets high-ranking employees like senior executives and financial officers. Such cyber attacks aim to steal a company’s sensitive information or funds.
- Vishing, also known as “voice phishing,” is a cyber crime aiming to steal confidential information through phone calls. Vishing attacks are also getting more common. In 2021 alone, they increased 554% in volume.
- Clone phishing is an attack where cyber criminals copy previously received or legitimate emails containing links or attachments. However, the copied email will redirect you to a fake website or infect your device with malware.
Phishing attack examples
To better understand what phishing is and how it works, let’s look at several real-life examples of such cyber attacks.
- “Your password is about to expire.” This is probably the most common example of phishing letter. In this case, the email pretends to be sent by the Microsoft support team. However, when taking a closer look, you will notice a few suspicious details. In particular, such an email delivers a sense of urgency and seems very demanding.

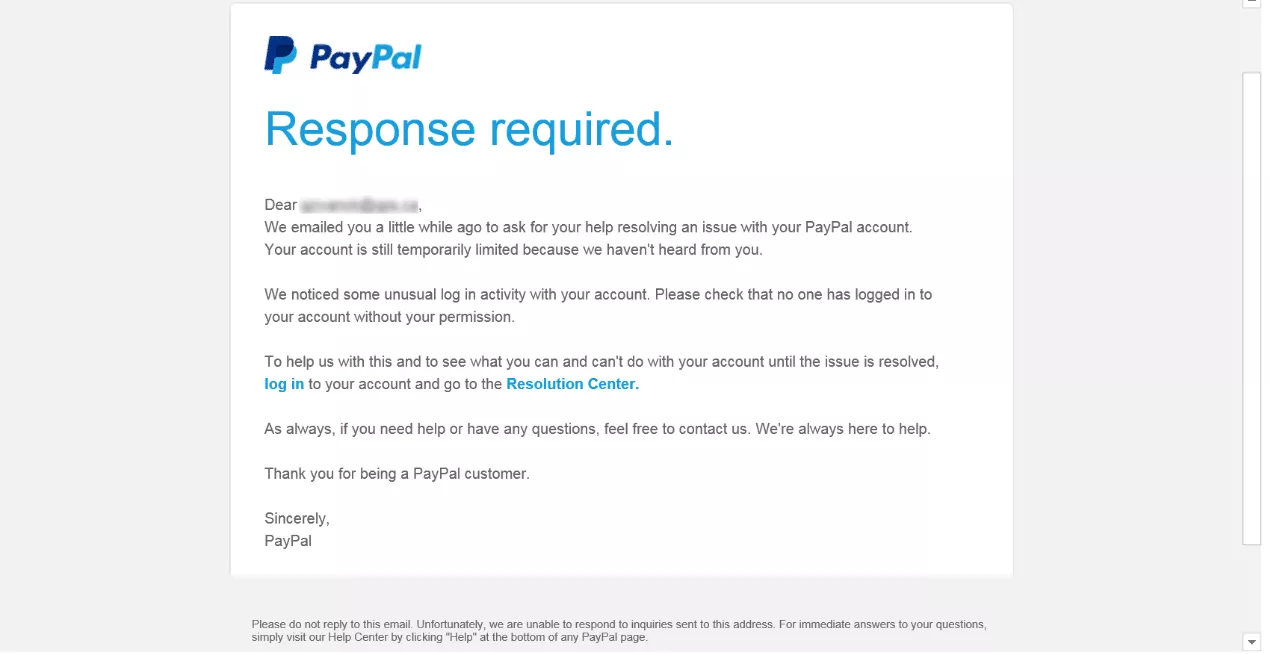
- “There’s an issue with your account.” Another common way to get a phishing victim hooked is to scare them or make them feel nervous. As an example, the image email attempts to convince the recipient that their PayPal account experiences “unusual log-in activity.”
How to prevent phishing emails?
The dangers of phishing attacks are pretty overwhelming, especially if you use multiple digital tools, social networks, and online banking systems. When receiving dozens of emails from various services daily, you risk dropping your guard and falling into a trap.
The following steps will help you feel more secure and prevent phishing attacks.
- Learn how to spot phishing scams. Be particularly careful of the alarming signs we’ve mentioned above.
- Check who’s the sender. Legitimate emails never come from an invalid address.
- Type URLs manually. Do not use the links provided in emails. Instead, check their validity and the “HTTPS” certificate in the URL.
- Find a way to secure your email account. Create a unique and strong password, regularly update your browser, and block suspicious emails.
- Do not respond to emails requesting personal information. Instead, turn to the service’s official support and ask for help.
- Report on emails you find suspicious. You can turn to an organization like Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and inform them about potential fraud.
- Use a reliable VPN provider like VeePN to block ads and fake websites. The VeePN tool ensures robust encryption and online security.
What is smishing?
Having learned the specifics and types of phishing, you probably wonder now what the definition of smishing is and whether it’s different from phishing. So let’s move on to another cyber threat we meant to discuss.
Smishing is a type of scam involving a fake SMS sent to a victim to steal their money or personal information. Like phishing, a smishing attack tries to convince you that a message you receive is legitimate and sent by a specific service, government agency, or bank. However, it may contain a malicious link or request for private data.
Hence, the difference between phishing and smishing lies not in their purpose but the means of attack. Phishing attacks typically appear as fake emails, while smishing scams are text messages sent to the victims’ phones.
Although SMS cyber attacks are less common than fake emails, the threat growth has become quite alarming. A recent survey claims that at the beginning of 2021, smishing attacks increased by 700%. So, it’s worth doing your best to recognize such threats. Here are the most noteworthy signs that will help you identify a smishing attack:
- Messages requiring an urgent reaction
- Suspicious SMS pretending to be legitimate
- Notifications asking to share personal data (credit card data, financial information, or else)
- The unknown sender, odd phone number (for example, 3000), or toll-free number (for example, 800)
- A “too good to be true” offer, lottery, or quiz containing a link
Smishing attack examples
Want to see what smishing attacks look like? We’ve got some for you! The following examples show the most common fake SMS you shouldn’t respond to.
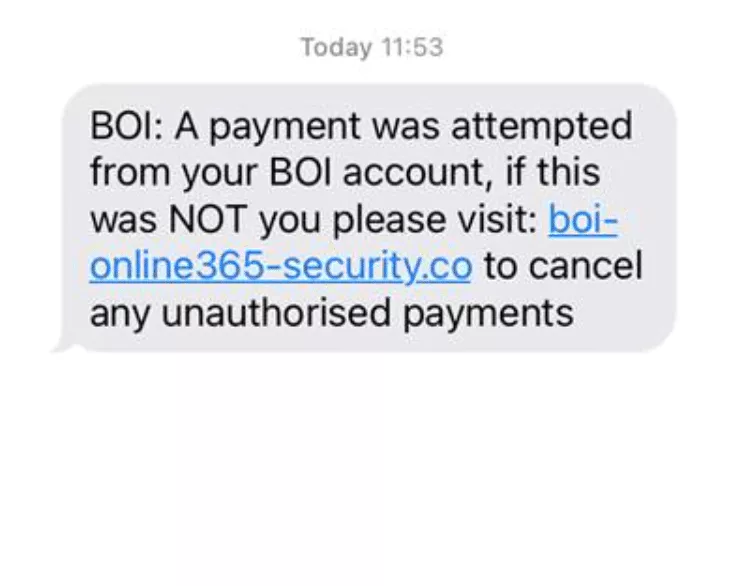
- “A payment was attempted from your bank account.” This SMS wants to make the recipient feel scared or confused. It claims that somebody is using the person’s account to make a purchase. Ignoring the provided link and calling official BOI support is the best way to detect such a scam.
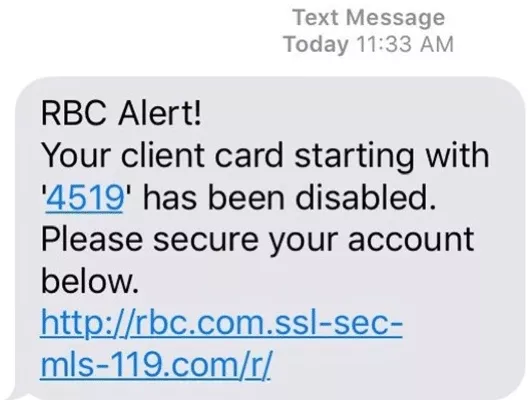
- “Your client card has been disabled.” This is another example of an SMS trying to force the recipient to act immediately. However, an attentive user will notice that the proposed URL is far from legitimate.
How to prevent smishing?
Preventing a cyber attack is always better than dealing with its consequences. Use the following tips to secure your phone and avoid smishing messages.
- Do not respond to suspicious texts. Any reply will likely open a can of worms.
- If a bank, company, or official institution claims to be the sender, call them directly. Instead of responding to the message, visit the official website.
- Do not click any links in the message. They aim to install malware on your phone and use it to steal your confidential information or even spy on your phone.
- Go online and check the sender’s phone number. Thanks to other victims’ reports, it may be mentioned as untrustworthy.
- Use a powerful VPN mobile app like VeePN to ensure encryption and protect you from hackers. VeePN’s applications suit multiple devices and platforms, including iOS and Android.
Protect yourself from phishing and smishing attacks with VPN
Phishing, smishing, and other types of scams can severely affect your online security. Understanding how to spot those threats is vital. However, it’s also worth enhancing your devices with an effective VPN tool. How does it help? Let’s look at the most significant benefits of VPN when fighting against phishing and smishing.
- It prevents monitoring of your traffic. VPN solutions block browser hijacking, so that phishing links cannot redirect you to illegitimate and dangerous websites.
- It detects and blocks malicious websites. A well-functioning VPN tool will prevent you from visiting phishing websites and, as a result, protect you from viruses.
- It secures your Internet connection. A firewall can filter your traffic and protect your IP from cyber threats.
- It hides your email address from the bad guys. VPN ensures a private Internet connection, making it much harder for cyber criminals to find your address and send fake messages or emails.
If you want to keep your private data safe and protect yourself from scams like phishing and smishing, VeePN is an excellent solution. It involves robust AES-256 encryption along with reliable security protocols preventing any potential data leaks. On top of that, VeePN’s NetGuard feature will block malicious websites and trackers, keeping you safe on all devices. Check out VeePN to take control of your personal security and prevent any cyber threats, including scams.
FAQs
How to spot a phishing email?
A phishing email strives to look legitimate. However, several signs might help you recognize a scam:
- A sense of urgency
- Domain name and sender’s address mismatch
- Grammar and spelling mistakes
- Request for private data like credentials
- Suspicious attachments or links
What is an example of phishing?
Normally, a phishing email contains a false notification of events forcing you to act immediately. For instance, it might warn you that your credit card or account will be blocked. Or that your password is about to expire. Such emails also offer to click on a link or download an attached file, which likely contains malware.
Is smishing a type of phishing?
Smishing is a type of phishing attack spread via SMS notifications. The word “smishing” combines the terms “SMS” and “phishing.” The key phishing and smishing difference is the platform the hackers use to attack the targeted users. Traditional phishing uses emails, while smishing scams are conducted over mobile phone texts.
VeePN is freedom
Download VeePN Client for All Platforms
Enjoy a smooth VPN experience anywhere, anytime. No matter the device you have — phone or laptop, tablet or router — VeePN’s next-gen data protection and ultra-fast speeds will cover all of them.
Download for PC Download for Mac IOS and Android App
IOS and Android App
Want secure browsing while reading this?
See the difference for yourself - Try VeePN PRO for 3-days for $1, no risk, no pressure.
Start My $1 TrialThen VeePN PRO 1-year plan