What Is Subnet Mask and How to Find Subnet Mask?
A subnet is a physical segment of a TCP / IP network that uses IP addresses with a common network identifier. To subdivide a network into multiple subnets, you must use a different network ID for each segment. Unique subnet IDs are created by splitting the host ID into two groups of bits.
The first of them serves to identify a segment of the interconnected network, the second – to identify a specific node. This mechanism is called subnet working. It is not necessary on an isolated network (i.e., not connected to the Internet).
Understanding Subnet Masks
Definition of Subnet Mask
A subnet mask is a 32-bit number used in IPv4 (or 128-bit for IPv6) that divides an IP address into network and host portions. The network portion ensures that data packets reach the right network, while the host portion identifies a specific device on that network. Essentially, the subnet mask acts as a guide, telling the network which part of the IP address refers to the network and which part refers to the host. This division is crucial for routing data packets efficiently and ensuring they reach their intended destinations. Subnet masks are fundamental in network management, making it easier to maintain and organize the network. However, implementing subnet masks often requires additional hardware, such as routers, which can add to the overall cost of the network infrastructure.
Representation of Subnet Masks
Subnet masks are typically represented in a dot decimal system, which consists of 32 binary bits divided into four octets (8 bits each). For example, a common subnet mask for a Class C network is 255.255.255.0. In this representation, the first three octets (255.255.255) indicate the network portion, while the last octet (0) identifies the specific device or host on that network. This means that in a Class C network, the first 24 bits of the IP address are used for the network address, and the remaining 8 bits are used for the host address. This clear division helps in efficiently routing data packets to the correct network and then to the specific device within that network.
IP Address Classes
The class system is used to more rationally define the size of the network. It allows distinguishing which part of the IP address refers to the network number and the host number. The class system uses the value of the first bit of the address. But such that the meanings of these first bits of the address are indications of which class a particular IP address belongs to.
Consider the table below. There are ranges of network numbers, as well as the maximum number of nodes corresponding to each class of networks:
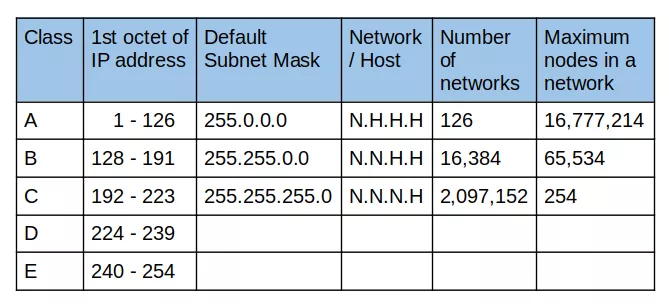
A Class B network uses the first two bytes for the network ID, allowing for a larger number of host addresses compared to Class C networks.
If the sequence 1110 is the beginning of the address, then this address belongs to class D. It designates a special, group address which is called multicast. If the destination address is a class D address, then such a package is available to all nodes to which this address is assigned.
Sequence 11110 at the beginning of the address specifies its belonging to class E. Addresses of this class are reserved for future applications. Thus, it becomes obvious that large networks are assigned class A addresses, medium – receive class B addresses, and small – class C. Class B networks can manage a range of hosts from 256 to 65,534, making them suitable for medium-sized networks. The network number can be represented by the first 8, 16, or 24 bits, and the host number – by the last 24, 16, or 8 bits. It all depends on what class the address belongs to.
Class C networks support a maximum of 254 hosts, making them ideal for smaller networks.
Subnet Masks in IP Addressing
We have already considered the traditional scheme of distribution of the IP address on node number and network number. The classification is based on the concept of class. The first few bits of the address determine the class. In this regard, it becomes obvious that since the first byte of the address 185.23.44.206 falls in the range 128-191, this address belongs to class B. The first two bytes, which are supplemented by two zero bytes 185.23.0.0, are the network number. Accordingly, the node number will be – 0.0.44.206. Experts note that determining the network numbers by the first bytes of the address also cannot be called a flexible and efficient mechanism for addressing. Therefore, it is recommended to allocate another feature that would help more flexibly define the boundary between the node number and the network number.
Each IP address class has a default subnet mask that helps identify the network address and the number of usable IP addresses within that subnet.
Subnet masks are widely used today as such a feature. A subnet mask is a binary number that contains units in those bits that belong to the extended network prefix. The subnet mask allows dividing the IP address into two main parts: the subnet number and the number of host addresses. The mask describes the address space of the subnet, from which address the subnet begins and which ends. The mask is widely used in conjunction with the IP address but does not replace it. It is possible to allocate a node number from a network number by means of a mask quickly and effectively. The binary mask entry includes ones in those bits that are signified as the network number in the IP address and zeros in those bits that are defined as the host number. Each class has its own IP address. And it is usually used by default.
The subnet mask describes the network address space, defining the range of addresses that belong to the subnet.
The network number is the whole part of the address. Consequently, the ones in the subnet mask must represent a continuous sequence.
For example, the address 185.23.44.206 corresponds to the mask 255.255.255.0. Therefore, the network number will be 185.23.44.0, although the rules of the class system establish a 185.23.0.0 network number.
Subnetting and Network Addresses
How Subnetting Works: Description of Binary Structure and Network-Device Identification.
Subnetting is a technique used to divide a large network into smaller, more manageable sub-networks, each with its own unique network address. This process involves using a subnet mask to split the IP address into network and host portions. The subnet mask determines how many bits are used for the network address and how many are used for the host address. By doing so, subnetting allows network administrators to better manage network traffic and improve overall network performance.
When a data packet is sent over the network, the subnet mask is used to determine which network the packet belongs to. The packet is then routed to the appropriate subnet, where it is delivered to the destination host. This method not only ensures efficient data routing but also helps in reducing network congestion. Subnetting allows network administrators to allocate IP addresses more efficiently, as each subnet can have its own range of IP addresses, tailored to the specific needs of that subnet.
In large networks, subnetting is particularly beneficial as it helps to reduce network traffic and improve performance. By dividing the network into smaller sub-networks, subnetting can also enhance network security, as each subnet can be configured with its own security settings. This segmentation makes it easier to isolate and manage different parts of the network, thereby improving overall security.
Moreover, subnetting can help prolong the life of IPv4 addresses, which are limited in number. By dividing a single IP address into multiple subnets, network administrators can create more IP addresses, allowing more devices to connect to the network. This efficient use of IP address space is crucial in today’s increasingly connected world.
Overall, subnetting is an essential technique for managing network addresses and improving network performance. By using subnet masks to divide IP addresses into network and host portions, network administrators can create more efficient, secure, and scalable networks.
How to Find Subnet Mask? Methods to Detect a Subnet Mask on Different Devices (Windows, macOS, Linux).
In modern IP routing, the mask mechanism is quite common. Subnet masks are actively used for various purposes. Due to subnet masks, an administrator can easily structure his network. In this case, additional network numbers are not required from the service provider. By segmenting a larger network into smaller subnets, organizations can limit access to only certain network segments, effectively protecting the entire network from being compromised.
Using a mask mechanism, service providers quickly combine the address spaces of multiple networks. This is due to the introduction of so-called “prefixes,” which allows to reduce the volume of routing tables and improve the performance of the routers in general. If an attack occurs, only that network segment is impacted, protecting the remaining parts of the network from exposure to potential threats.
Administrators and many other people who need to master computer networks often have the question of how to find a subnet mask. We will talk about this in detail below. Subnetting also enhances security by controlling pathways for remote network access, ensuring that if one subnet is compromised, the impact is limited to that specific segment.
How to Detect a Subnet Mask if the IP Network Class is Known?
As mentioned above, there are five classes of IP addresses to date. It is not difficult to determine the class of an IP address. You just need to convert it to binary and pay attention to the beginning of the bit sequence. Based on this, you can set the subnet mask. Just remember the ranges that belong to the classes.
Is It Possible to Learn a Mask If a Prefix Is Known?
The mask is often written as a prefix, a practice that has been approved since the advent of CIDR, which simplifies subnet masking. It indicates the number of bits in the network. The system of prefixes has been approved for a long time since the advent of CIDR. Its advantage is the absence of the need for classes, as well as the use of any number of IP bits to identify the network. If the prefix is known, you can easily set the subnet max according to the corresponding table.
In conclusion, we should note that it is also possible to find the subnet mask by using a VPN. This is an effective and fairly reliable method that many people use today.
FAQ
A subnet mask is a numerical label used in IP networking to divide an IP address into the network and host portions. It determines which part of the address identifies the network and which part identifies devices within that network. Subnet masks are essential for efficient IP address allocation, enabling network segmentation, and ensuring secure and manageable communication.
A subnet mask improves network security by segmenting a larger network into smaller, isolated subnets. This limits broadcast traffic, making it harder for unauthorized devices to access the entire network. By restricting communication between subnets, it also reduces the attack surface, helping to contain potential threats within a specific segment.
An IP address identifies a device on a network and consists of a network and host portion. A subnet mask, on the other hand, defines which part of the IP address is allocated to the network and which part is for devices (hosts) within that network. While the IP address is unique to each device, the subnet mask is a configuration tool used to group devices within a network.
Subnet masks improve network performance by reducing broadcast traffic and isolating network segments. By dividing a large network into smaller subnets, they limit the scope of data sent to all devices, minimizing congestion. This segmentation helps optimize bandwidth and reduces the likelihood of network slowdowns due to excessive traffic.
Yes, classful and classless subnet masks differ in how they allocate IP addresses. Classful subnet masks adhere to predefined address classes (A, B, or C), limiting flexibility and leading to inefficient IP usage. Classless subnet masks, used in CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing), allow more granular subnetting by specifying custom prefix lengths, improving address allocation and enabling more efficient use of IP space.
VeePN is freedom
Download VeePN Client for All Platforms
Enjoy a smooth VPN experience anywhere, anytime. No matter the device you have — phone or laptop, tablet or router — VeePN’s next-gen data protection and ultra-fast speeds will cover all of them.
Download for PC Download for Mac IOS and Android App
IOS and Android App
Want secure browsing while reading this?
See the difference for yourself - Try VeePN PRO for 3-days for $1, no risk, no pressure.
Start My $1 TrialThen VeePN PRO 1-year plan