The State of Data Tracking in 2025: How Companies Are Watching You & How to Stop Them
“If you gaze long into an abyss, the abyss also gazes into you.”
In 2025, the abyss has a name: data tracking. While we scroll, search, swipe, and stream, corporations and governments sit quietly behind the curtain, watching back, tallying every tap, dissecting every digital breadcrumb.
We do live in the age of surveillance capitalism, where data tracking has evolved into a fine-tuned machine, watching, recording, and shaping your digital life in ways you may not even notice. In this article, we’ll explore how companies are watching you in 2025, the real impact on your privacy, and how you can take back control before the gaze of the abyss becomes inescapable.
The abyss has dozens of eyes. Modern tracking technologies described
There are numerous ways companies, advertisers, and governments are watching you while you peacefully browse the web, scroll your feed on social media, or just use your running app to track your fitness progress. Let’s review the most common data tracking examples:

Device fingerprinting
Every device connected to the Internet, be it fitness watches, a laptop, a tablet, or your smart TV, has its own operating system that communicates with servers. In such a way, together with essential data, your devices share other information such as usage time, frequency of features use, or even what content you prefer. All this information gets into the hands of advertisers and search engines to target you with relevant ads. Even though you may encounter product offers you can be really interested in, companies know way too much about you.
ISP tracking
Internet service providers (ISPs) are one of the most pesky watchers of your online activities. A so-called Utiq technology enables ISPs to collect more data than just your browser cookies, so that ISPs can see your online activity across multiple websites to create your distinct profile based on usage patterns and behaviors. As a result, you may face connection speed throttling because your ISP thinks streaming your favorite show in 4K quality or online game eats up the network bandwidth. Also, you may get spammed with ads as the ISP has sold your data to an advertising agency.
Email tracking pixels
Another tricky technique used to track your online behaviors. Tracking pixels, often called web beacons or pixel tags, are tiny, hidden images embedded in emails, web pages, and other digital content. Marketers frequently use them to monitor how users engage with websites, emails, and social media. But these pixels can also be misused for malicious activities and pose substantial data security threats.
The main risk of email tracking pixels is that they’re used without your consent, so such a beacon can collect information about your IP address, location, and the device you’re using. Needless to say, such information does help cybercriminals to create well-prepared spear phishing attacks.
Browser fingerprinting
Just like device fingerprinting, your web browser is also subject to detailed profiling. Sites you visit, what you google, how much time you spend surfing the web, and so on create your distinct online profile that advertisers, companies, and governments can access. But what if this information leaks to scammers? Phishing attempts, account breaches, or identity theft are the most obvious cons of browser tracking.
Mobile SDK tracking
Mobile apps are rarely developed from scratch as it would take much time and effort. Instead, mobile developers use software development kits (SDKs) to create an application with ready-made tools. And that’s where the shoe pinches!
Most SDKs contain entire libraries or individual application programming interfaces (APIs) to exchange with various companies and services such as Amazon, Meta, or Google. A mobile developer may create just an innocent gamification app of your walking activity while one of its embedded code libraries is programmed to collect your location data, app usage time, and other information. The amount of this information is shocking, to say the least. But more on that later, as we have to discuss a couple of other tracking techniques.
Geofencing
Geofencing is a location-based technology that creates virtual boundaries or “fences” around specific geographic areas. When a user’s device enters, leaves, or remains within these boundaries, an app or system can trigger a particular action such as sending a notification, collecting relevant usage data, or delivering targeted content. Businesses commonly use geofencing for marketing campaigns, loyalty programs, and proximity-based alerts, while security and logistics sectors leverage it for asset tracking and access control.
At its core, geofencing relies on GPS, WiFi, cellular data or even radio frequency identification (RFID) signals to track where you are in real time. When you integrate that with a mobile app, you can get personalized experiences like deals suggested when you walk into a specific zone, or reminders sent when you enter that zone. But that also raises questions about data collection and misuse.
Third-party ad scripts
Third-party ad scripts are pieces of code from external ad networks or platforms that are placed on websites to show ads, track user interactions and gather analytics. These scripts often use cookies and other tracking methods to serve personalized ads based on a user’s browsing behavior and demographic profile. As they come from external servers rather than the website you’re visiting directly, they can bypass some security measures and potentially involve performance and privacy risks.
For businesses, third-party ad scripts make it easy to integrate ad solutions without building their own ad infrastructure. But this convenience comes at the cost of website owners losing some control over what data is collected and how it’s used. Malicious actors can occasionally exploit these scripts to inject malware or inappropriate content.
Form and input tracking
Form and input tracking means monitoring user interactions with online forms, like text fields, drop-downs and other form elements. By recording keystrokes, clicks or partial inputs even before the user hits “Submit”, companies can see where users are getting stuck or bailing. This helps businesses optimize user experiences, diagnose usability issues and gain insights into user behavior.
But form and input tracking can raise privacy and security concerns, especially when sensitive personal data is being collected or stored. If not done with transparency, consent and protection, this data can be accessed by unauthorized parties or misused for unethical profiling.
The tracking abyss does have a lot of eyes to gaze at you at different angles and depths. Beyond a doubt, these gazes bear inherent risks we need to discuss for you to understand how dangerous online data tracking can be.
The risks of falling into the tracking abyss
When the tracking abyss gazes at you with such a determination, you’re likely to fall into it. This fall carries a range of such risks as:

Privacy loss
Your Internet privacy is no longer safe as marketing businesses, corporations, governments, and even your local ISP know what you read, watch, listen to, what your interests are, and whether you have a romantic partner. Privacy is a genuinely basic human right, but information tracking deprives us of it, so hiding your life from prying eyes is a precious privilege nowadays.
Financial and identity theft
In addition to invasion of privacy, you risk losing your money and your good name. Imagine data breach happens, and your sensitive information gathered by third parties leaks to fraudsters. They can use it to breach your banking accounts and steal your savings or just impersonate you for phishing, stalking, or damaging your reputation by publishing embarrassing/fake information about you.
Manipulative advertising and price discrimination
Since advertisers and companies know so much about you, they can use this information to target manipulative ads to you. For example, you spend an evening researching stress management techniques. You visit several mental health blogs, watch a few anxiety-related videos on YouTube, and skim through articles about meditation apps. As you browse, advertising networks place tracking cookies and run scripts on these sites to gather data about your interests and concerns.
Within a day, you start seeing ads specifically offering “instant mood boosters,” “anxiety quick fixes,” or even products claiming miraculous mental health benefits, often in eye-catching, urgency-driven formats. Because advertisers know you’ve been reading about stress and mental health, they tailor these ads to your potential emotional vulnerability. This can be considered manipulative because it exploits personal or sensitive information, collected silently in the background, to push products or services at precisely the moment you’re most vulnerable.
In the same vein, knowledge about your online behaviors, purchase habits, average amount of money spent on online shopping, and such enables online shopping sites and booking services to increase prices on their products and services. By knowing how much you spend regularly, they treat you as one who can afford overpaying a particular amount for a desired item/service.
Phishing attacks probability
When so much data about you can be possibly leaked, it’s no wonder fraudsters will use it to plan a sophisticated phishing attempt, so that you may have little chance to notice it’s a scam. Staying vigilant all the time is impossible, which is why such a leak of your sensitive information increases the chances you’ll miss a strike one day.
Potential chilling effects
On top of all these risks, tracking can seriously intimidate you from participating in political activism and expressing your opinion on important topics online as you may fear this information will be used against you. Generally speaking, a feeling that you’re constantly watched deprives you of the ability to act and speak freely without being concerned for potential negative consequences.
Are these fears justified?
The risks of online tracking we’ve just discussed aren’t abstract concepts that don’t have any impact on security and privacy of users. In fact, the extent of tracking influence is jaw-dropping.
To start with, let’s take a look at the most popular websites such as Amazon, Wikipedia, YouTube, X (formerly Twitter), and others. On average, each site has 2-3 trackers used for advertising, while Amazon leads with 17 trackers focused on collecting your data for commercial purposes.
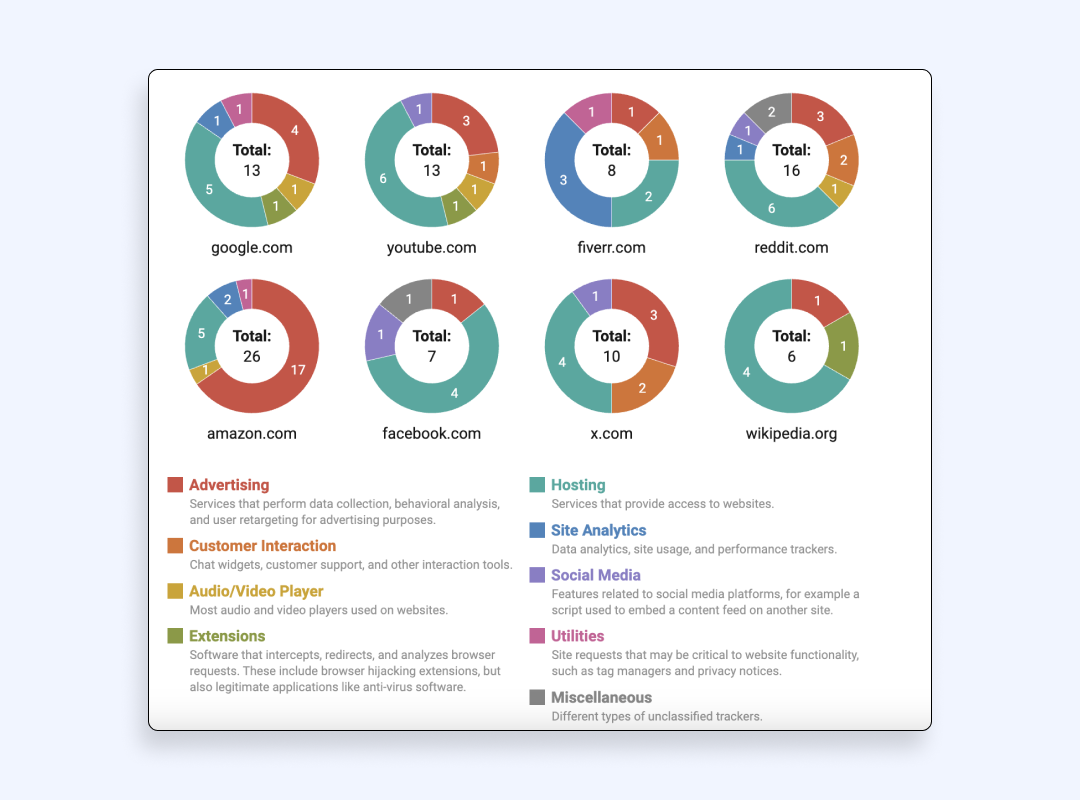
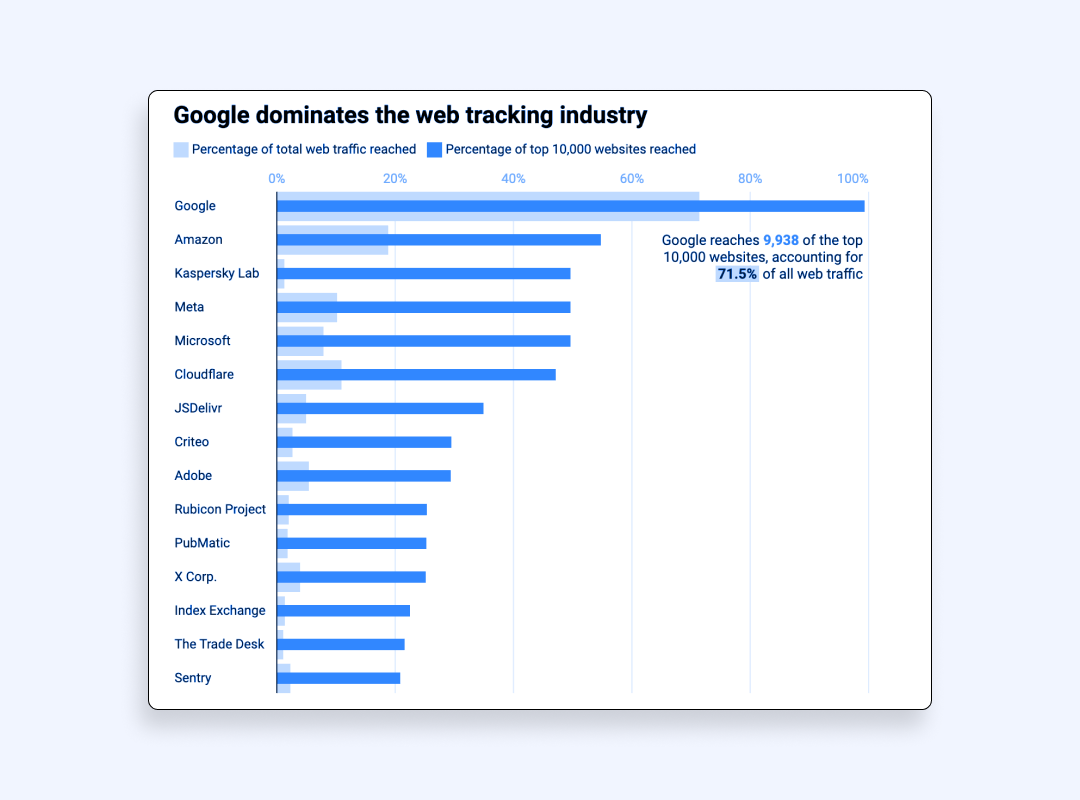
On top of that, the problem extrapolates to the entire web and gets only worse. If you go to one of the top-10,000 visited sites, you’re likely to get tracked by 12 services. For example, Google Static is active on 9,000 out of 10,000 top popular sites. Actually, Google appears to be the most widespread company collecting your personal information one way or another. In the above-mentioned top 10,000 sites, there are only 62 sites that aren’t connected to any of Google’s trackers! Meta doesn’t look so evil any longer, does it?
Speaking about mobile platforms, iOS, which is commonly considered more private and secure than the open-source Android operating system, isn’t a saint as well. 82.78% of iOS apps track user data, while free applications collect 4 times more information than paid ones.
Under these circumstances, 75% of consumers claiming that tech companies have too much control over their data doesn’t sound that paranoid. Furthermore, 85% of users intend to improve their online security and privacy measures to stay more protected.
We can only encourage such a desire and want to help you take care of your online security, too. Up next, we’re going to discuss the most essential tips on how to resist falling into the online tracking abyss to reduce its influence on your life.
How to avoid hitting the abyss bottom
To minimize exposure of your personal information to online trackers, we highly recommend following these steps:

🫣Manage tracking settings. Go check your browser settings and switch off any options related to data collection. It includes third-party cookies, tracking features, and the like.
🫣Clear cookies and block trackers. Clear your cookies and cache from time to time to ensure websites can’t read them. Additionally, use ad blockers to prevent tracking targeted ads. For example, VeePN has a built-in ad blocker and anti pop-up feature that can provide you with private and comfortable browsing.
🫣Be cautious with permissions. Always pay attention to the app permissions you grant on your device. Avoid letting the apps access your media, contacts, geolocation, and other data not essential for proper functioning of this app.
🫣Use privacy-focused browsers. Such browsers as TOR, Brave, or Firefox enable you to surf the web anonymously. Consider using one of them, but don’t give up on other privacy and security measures, as no browser will guarantee you 100% anonymity if you act carelessly.
🫣Limit social media tracking and opt out from targeted advertising. Disable any tracking in your social media settings and opt out from targeted ads whenever possible to reduce the chances of being spammed with tons of ads targeted at you.
🫣Use a temporary disposable email and phone number. Don’t use your personal email and phone number to sign up for sites and online services. Instead, consider using Anonymous Email and Online Free SMS tools by VeePN that will help you avoid using your personal information.
🫣Turn off location services. Most of your apps use location services, so you need to switch them off to disable these apps from sharing your location data. For advanced privacy, turn off geolocation on your device. Check our related articles on how to do it on your iOS or Android device.
🫣Use a virtual private network (VPN) app. By using a VPN app, you pass all your Internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel that leads to a remote server. In such a way, you can prevent tracking online and conceal your identity as nobody can see your real location and what you’re doing on the web. We recommend you avoid free VPN apps as they still share your sensitive information with third parties. That’s why we would like to introduce VeePN, a premium VPN app that offers robust privacy features to ensure your online exposure is as minimal as possible. Let’s discuss these benefits in more detail!
Why VeePN can be your safety rope
VeePN is an all-in-one cybersecurity app that can become your reliable instrument for ensuring your data protection and privacy online, owing to such features as:
🛡️Strong encryption. VeePN uses military-grade AES-256 encryption, which scrambles your data into unreadable code during transmission. This means even if a hacker or ISP intercepts your traffic, they won’t be able to decipher any personal information, browsing history, or downloads. It’s particularly effective on unsecured public WiFi networks as your emails, banking data, and even conversations remain private.
🛡️No Logs policy. We commit ourselves to a strict policy of not collecting and selling your personal information for commercial purposes.
🛡️Device compatibility. VeePN supports all major platforms: Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, Linux, and browser extensions for Chrome and Firefox. You can protect up to 10 devices simultaneously with a single account.
🛡️Alternative ID. With this feature, you can create an alternative persona to create profiles for social media, sites, and online stores to keep your real identity hidden.
Download VeePN today and enjoy a 30-day money-back guarantee!
FAQ
Companies use tools like cookies, browser fingerprinting, device tracking, and AI-based behavior analysis to monitor your actions across websites, apps, and even smart devices. Check out this article for more information.
Yes, but with limitations. Most countries have regulations like GDPR or CCPA, yet many companies still find loopholes to collect and use your data without clear consent.
Use a reliable VPN such as VeePN, block third-party cookies, adjust app permissions, and browse in private modes. Combining these steps significantly reduces your digital footprint.
VeePN is freedom
Download VeePN Client for All Platforms
Enjoy a smooth VPN experience anywhere, anytime. No matter the device you have — phone or laptop, tablet or router — VeePN’s next-gen data protection and ultra-fast speeds will cover all of them.
Download for PC Download for Mac IOS and Android App
IOS and Android App
Want secure browsing while reading this?
See the difference for yourself - Try VeePN PRO for 3-days for $1, no risk, no pressure.
Start My $1 TrialThen VeePN PRO 1-year plan