IPv4 vs IPv6: Understanding Key Differences, Benefits, and Why It Matters
When there is a shortage of IP addresses, people have to design a new internet protocol and save the world from this problem. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is responsible for the development and introduction of IPv6. It is how IPv6 stepped in after the operating of its predecessor, IPv4. It was invented in the ‘90s and provided new unique addresses. Actually, the offered amount is enough even in case each individual has lots of devices. However, IPv6 is still not fully implemented. The reasons are below:
There is no compatibility with IPv4
You can’t enter the site if it is running on IPv4 while ISP and your device are using the newer protocol. In this situation, all ISPs, operating systems, and devices must upgrade their systems. Otherwise, a seamless worldwide shift is impossible. Your devices need to be compatible with both protocols to avoid possible service disruption. Unfortunately, this requires extra investments and is too costly.
No clear benefits for every user
It is rather challenging for the companies to explain to the clients the necessity of investment in another technology if they can’t see the direct impact. Only if people feel the actual shortage of IP addresses will they understand the value of using new technology, thus creating more IP addresses.
Understanding IP and VPN Basics
What is IP?
IP, or Internet Protocol, is the backbone of the internet, governing how data is routed across networks. It sets the rules for how devices communicate and exchange information, ensuring that data packets reach their intended destinations. Each device or domain on the internet is assigned a unique IP address, which serves as its identifier. These IP addresses can be numeric, as seen in IPv4, or alphanumeric, as in the case of IPv6. The primary role of IP addresses is to facilitate the identification and location of devices on a network, making seamless communication possible.
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology designed to create a secure and encrypted connection between a device and a network over the internet. By using IP addresses, VPNs establish a secure tunnel that protects data from prying eyes, ensuring that users can browse the internet privately and securely. One of the key benefits of a VPN is its ability to mask IP addresses, making it difficult for third parties to track online activities. This added layer of security is particularly valuable for maintaining privacy and protecting sensitive information from potential cyber threats.
IPv4 & IPv6: Key Differences and Larger Address Space
IPv6 doesn’t only solve the issue of IP addresses shortage, but it comes with more advantages in comparison to IPv4. Here are the major ones:
- Absence of geographical limitations. IPv6 guarantees access to every part of the world, unlike IPv4. Hence everybody will be able to use it, unlike IPv4 addresses. Back in the time of the technology development, half of all addresses were reserved for the USA.
- Enhanced security. Security is a top priority for IPv6. It provides authentication, advanced confidentiality, and data integrity.
- Auto-configuration. It is one of the best IPv6 features. Auto-configuration lets the devices assign IP addresses on their own and do not use a server. Thanks to the MAC address, the devices can easily connect to the same network while discovering each other.
- End-to-end connectivity. IPv6 doesn’t require using NAT that engineers created to cope with the lack of IP addresses. It allows all devices to connect to the Internet and deal with every site directly.
- More effective routing. IPv6 has persistent headers, while IPv4 headers are variable in lengths. As a result, the code for routing is simpler and does not require much hardware. In simpler words, IPv6 provides better service quality and enhanced user experience. IPv6 includes a flow label field in its header for packet flow identification, which enhances network traffic management.
IPv4 and IPv6 Fundamentals
IPv4 Overview
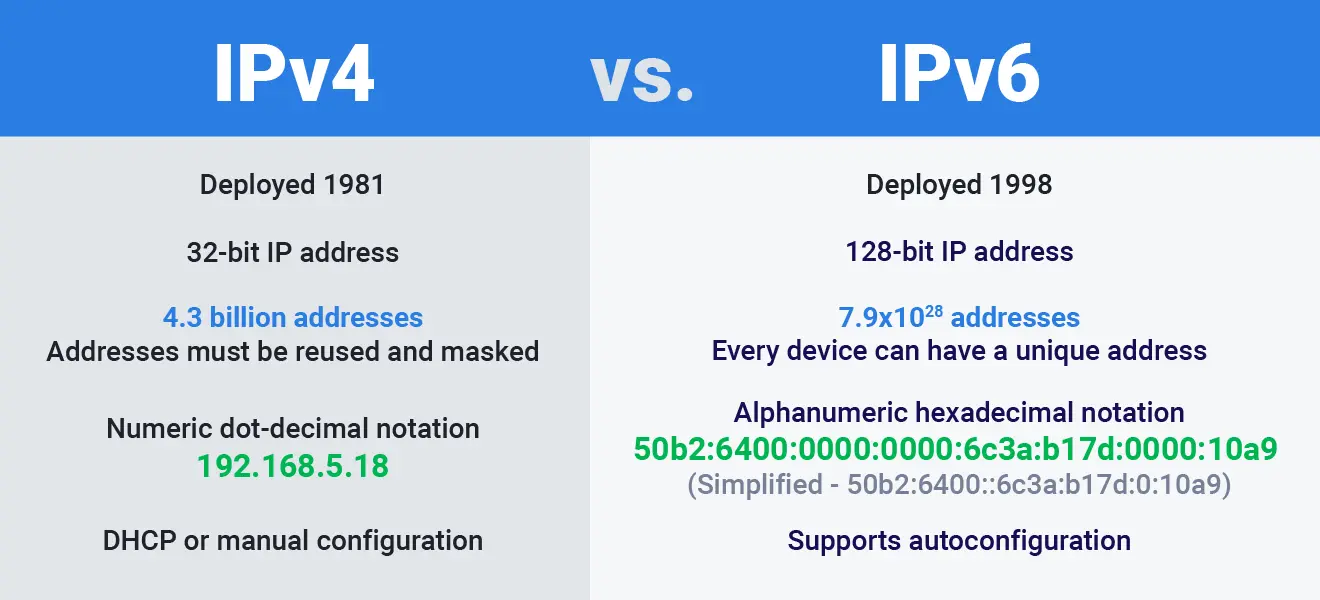
IPv4, the original version of the Internet Protocol, was launched in 1983 and has been the foundation of internet communication ever since. It uses a 32-bit address format, which provides approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. Despite its widespread use, IPv4 has several limitations, including a limited address space and the need for Network Address Translation (NAT) to conserve addresses. IPv4 addresses are numeric and separated by periods, such as 192.168.0.1, and they play a crucial role in identifying devices on a network and routing data packets to their destinations.
One of the key features of IPv4 is its simple virtual communication layer, which enables seamless communication between devices. However, this simplicity also leads to unnecessary network traffic and a limited address space, which has become a significant challenge as the number of connected devices continues to grow. To manage IP address assignment, IPv4 often relies on the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), which automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network, simplifying network management.
In terms of security, IPv4 has some inherent limitations, as it lacks built-in security features. However, Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) can be used to provide encryption and authentication for IPv4 traffic, enhancing network security. IPSec is a suite of protocols that ensures secure communication over the internet, making it a valuable tool for protecting IPv4 traffic.
Overall, IPv4 has been instrumental in the development of the internet, but its limitations have paved the way for the adoption of IPv6. With its larger address space, improved security features, and enhanced performance, IPv6 addresses many of the challenges associated with IPv4, making it a more scalable and secure solution for the future of internet communication.
Speed Comparison: IPv4 vs IPv6
If you are wondering whether IPv6 is faster than its predecessor, then mind, it is not. Devices communicate and agree on which IP version to use during their interaction, which can impact speed performance. According to the recent testing in which 22 domains from 6 various locations were involved, IPv6 is slower. In fact, the difference is not huge, and the results admit only a fraction of a second that ordinary users will not even notice. The testers state that the speed may depend on the location.
Peculiarities of IPv6 VPN and Network Address Translation
Most of the VPN software works on IPv4. IP plays a crucial role in enabling seamless communication between devices on a network. Therefore, if you try to access the site which runs on IPv6, your VPN server will redirect the traffic to an external IPv6 DNS server. It means that traffic will not be secure anymore as it exits a safe VPN tunnel. Here when the worst thing may happen. Your original IP address and your location will be exposed because of susceptibility to a DNS leak. Moreover, the resource that you are visiting may suffer from further problems. ISP is able to monitor all your online activities, defeating the aim of using a VPN server. It would be rather difficult to detect the following leaks without using a DNS leak test.
You can avoid it with DNS leak protection that a reliable server VeePN offers. VeePN router DNS requests through an encrypted tunnel and does not interact with external DNS providers. This allows you to provide complete protection for traffic as well as DNS queries. You should realize that securing your traffic without guarding DNS queries is simply pointless.
Summing – up: Internet Protocol Security
With the fast incorporation of modern technologies in all spheres of a person’s life, it is not surprising that each person has dozens of devices. An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a unique numerical identifier assigned to devices on a network. This is when the problem of unique IP addresses may seem to be very serious and require an efficient solution. Luckily, the technology IPv6 has solved this issue. IPv6 is the latest internet protocol version, offering significant improvements over IPv4. Its key features are:
- Quality service support (QoS)
- A perfect protocol for neighboring node interaction
- Hierarchical addressing
- Stateless and stateful configuration
- Routing infrastructure
The differences between IP version 4 and IP version 6 include advancements in address structure and security features.
Together with VPN software, a user can safely surf the website and not worry about losing personal information thanks to DNS leak prevention.
FAQ
IPv4 uses a 32-bit address, while IPv6 uses a 128-bit address, allowing vastly more unique addresses.
Yes, through dual-stack systems and tunneling methods, though not all networks support these solutions.
IPv6 can be faster than IPv4 in some cases because it eliminates the need for NAT (Network Address Translation) and has larger address spaces, which can simplify routing. However, the actual speed difference depends on factors like the network infrastructure and ISP support. In many current setups, the performance difference is negligible for most users.
Not all VPNs support IPv6, as many primarily handle IPv4 traffic. Some VPNs block IPv6 to prevent IPv6-related leaks, while others fully support it by tunneling both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic securely. If IPv6 support is important, choose a VPN that explicitly states it manages IPv6 connections effectively.
IPv6 supports IPsec, offering better encryption and authenticity verification than IPv4 by default.
VeePN is freedom
Download VeePN Client for All Platforms
Enjoy a smooth VPN experience anywhere, anytime. No matter the device you have — phone or laptop, tablet or router — VeePN’s next-gen data protection and ultra-fast speeds will cover all of them.
Download for PC Download for Mac IOS and Android App
IOS and Android App
Want secure browsing while reading this?
See the difference for yourself - Try VeePN PRO for 3-days for $1, no risk, no pressure.
Start My $1 TrialThen VeePN PRO 1-year plan